服务热线
135-6963-3175
Sentinel原理-滑动窗口
最重要的一个Slot非StatisticSlot莫属,因为他做的事是其他所有的Slot的基础。包括各种限流,熔断的规则,都是基于StatisticSlot统计出来的结果进行规则校验的。
我们先来看一段非常熟悉的代码,就是StatisticSlot中的entry方法:
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, Object... args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 触发下一个Slot的entry方法
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
// 如果能通过SlotChain中后面的Slot的entry方法,说明没有被限流或降级
// 统计信息
node.increaseThreadNum();
node.addPassRequest();
// 省略部分代码
} catch (BlockException e) {
context.getCurEntry().setError(e);
// Add block count.
node.increaseBlockedQps();
// 省略部分代码
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
context.getCurEntry().setError(e);
// Should not happen
node.increaseExceptionQps();
// 省略部分代码
throw e;
}
}StatisticSlot中就是做了三件事:
1.通过node中的当前的实时统计指标信息进行规则校验
2.如果通过了校验,则重新更新node中的实时指标数据
3.如果被block或出现了异常了,则重新更新node中block的指标或异常指标
可以很清晰的看到,所有的实时指标的统计都是在node中进行的。
DefaultNode和ClusterNode
//node.addPassRequest() //这里的node是一个 DefaultNode 实例
@Override
public void addPassRequest() {
super.addPassRequest();
this.clusterNode.addPassRequest();
}其实都是执行的 StatisticNode 对象的 addPassRequest 方法
//每秒的实时统计信息,使用 ArrayMetric 实现,即基于滑动窗口实现,默认1s 采样 2次。
//即一个统计周期中包含两个滑动窗口。
private transient Metric rollingCounterInSecond = new ArrayMetric(1000 / SampleCountProperty.sampleCount, IntervalProperty.INTERVAL);
//每分钟实时统计信息,同样使用 ArrayMetric 实现,即基于滑动窗口实现。每1分钟,抽样60次。
//即包含60个滑动窗口,每一个窗口的时间间隔为 1s 。
private transient Metric rollingCounterInMinute = new ArrayMetric(1000, 2 * 60);
@Override
public void addPassRequest() {
rollingCounterInSecond.addPass();
rollingCounterInMinute.addPass();
}Metric
从代码中我们可以看到,具体的增加pass指标是通过一个叫 Metric 的接口进行操作的,并且是通过 ArrayMetric 这种实现类,现在我们在进入 ArrayMetric 中看一下。
public class ArrayMetric implements Metric {
/**
* 用来存储各个窗口的数据
*/
private final LeapArray<MetricBucket> data;
/**
*
* @param sampleCount 在一个采集间隔中抽样的个数,默认为 2,
* 例如当 intervalInMs = 1000时,抽象两次,则一个采集间隔中会包含两个相等的区间,
* 一个区间就是滑动窗口。
* @param intervalInMs 表示一个采集的时间间隔,例如1秒,1分钟。
*/
public ArrayMetric(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {
this.data = new OccupiableBucketLeapArray(sampleCount, intervalInMs);
}
/**
*
* @param sampleCount
* @param intervalInMs
* @param enableOccupy 是否允许抢占,即当前时间戳已经达到限制后,是否可以占用下一个时间窗口的容量,
* 这里对应 LeapArray 的两个实现类,如果允许抢占,则为 OccupiableBucketLeapArray,
* 否则为 BucketLeapArray。
*/
public ArrayMetric(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs, boolean enableOccupy) {
if (enableOccupy) {
this.data = new OccupiableBucketLeapArray(sampleCount, intervalInMs);
} else {
this.data = new BucketLeapArray(sampleCount, intervalInMs);
}
}
@Override
public void addPass(int count) {
WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow();
wrap.value().addPass(count);
}
.....
}wrap.value().addPass() 是执行的 wrap 对象所包装的 MetricBucket 对象的 addPass 方法,这里就是最终的增加qps中q的值的地方了。进入 MetricBucket 类中看一下,具体的代码如下:
public class MetricBucket {
private final LongAdder[] counters;
private volatile long minRt;
public MetricBucket() {
MetricEvent[] events = MetricEvent.values();
this.counters = new LongAdder[events.length];
for (MetricEvent event : events) {
counters[event.ordinal()] = new LongAdder();
}
initMinRt();
}
public void addPass(int n) {
add(MetricEvent.PASS, n);
}
public MetricBucket add(MetricEvent event, long n) {
counters[event.ordinal()].add(n);
return this;
}
...
}再看下枚举类MetricEvent:
public enum MetricEvent {
/**
* Normal pass.通过数量
*/
PASS,
/**
* Normal block.阻塞数量
*/
BLOCK,
/**
* 异常数量
*/
EXCEPTION,
/**
* 成功数量
*/
SUCCESS,
/**
* 响应时间
*/
RT,
/**
* Passed in future quota (pre-occupied, since 1.5.0).
*/
OCCUPIED_PASS
}LongAdder:
public class LongAdder extends Striped64 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7249069246863182397L;
/**
* Version of plus for use in retryUpdate
*/
@Override
final long fn(long v, long x) { return v + x; }
/**
* Creates a new adder with initial sum of zero.
*/
public LongAdder() {
}
/**
* Adds the given value.
*
* @param x the value to add
*/
public void add(long x) {
Cell[] as;
long b, v;
HashCode hc;
Cell a;
int n;
if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) {
boolean uncontended = true;
int h = (hc = threadHashCode.get()).code;
if (as == null || (n = as.length) < 1 ||
(a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null ||
!(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x))) { retryUpdate(x, hc, uncontended); }
}
}
/**
* Equivalent to {@code add(1)}.
*/
public void increment() {
add(1L);
}
....
}所以是通过LongAdder 来保存各种指标的值的。
接下来进行data.currentWindow()分析:
参数为当前时间戳
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {
if (timeMillis < 0) {
return null;
}
/**
* 计算当前时间会落在一个采集间隔 ( LeapArray ) 中哪一个时间窗口中,
* 即在 LeapArray 中属性 AtomicReferenceArray > array 的下标
*/
// idx被分成[0,arrayLength-1]中的某一个数,作为array数组中的索引
int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);
// Calculate current bucket start time.
/**
* 计算当前时间戳所在的时间窗口的开始时间,即要计算出 WindowWrap 中 windowStart 的值,
* 其实就是要算出小于当前时间戳,
* 并且是 windowLengthInMs 的整数倍最大的数字,Sentinel 给出是算法为 ( timeMillis - timeMillis % windowLengthInMs )。
*/
long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);
/*
* Get bucket item at given time from the array.
*
* (1) Bucket is absent, then just create a new bucket and CAS update to circular array.
* (2) Bucket is up-to-date, then just return the bucket.
* (3) Bucket is deprecated, then reset current bucket and clean all deprecated buckets.
*/
//死循环查找当前的时间窗口,这里之所有需要循环,是因为可能多个线程都在获取当前时间窗口。
while (true) {
// 从采样数组中根据索引获取缓存的时间窗口
WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);
// array数组长度不宜过大,否则old很多情况下都命中不了,就会创建很多个WindowWrap对象
if (old == null) {
/*
* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4
* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp
* ^
* time=888
*/
// 如果没有获取到,则创建一个新的
WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
/**
// 通过CAS将新窗口设置到数组中去
* 这里使用了 CAS 机制来更新 LeapArray 数组中的 元素,因为同一时间戳,可能有多个线程都在获取当前时间窗口对象,
* 但该时间窗口对象还未创建,这里就是避免创建多个,导致统计数据被覆盖,
* 如果用 CAS 更新成功的线程,则返回新建好的 WindowWrap ,CAS 设置不成功的线程继续跑这个流程,然后会进入到代码。
*/
if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {
// 如果能设置成功,则将该窗口返回
return window;
} else {
// 否则当前线程让出时间片,等待
// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.
Thread.yield();
}
// 如果当前窗口的开始时间与old的开始时间相等,则直接返回old窗口
} else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {
/**
* 如果指定索引下的时间窗口对象不为空并判断起始时间相等,则返回。
*/
/*
* B0 B1 B2 B3 B4
* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp
* ^
* time=888
* startTime of Bucket 3: 800, so it's up-to-date
*
* If current {@code windowStart} is equal to the start timestamp of old bucket,
* that means the time is within the bucket, so directly return the bucket.
*/
return old;
// 如果当前时间窗口的开始时间已经超过了old窗口的开始时间,则放弃old窗口
// 并将time设置为新的时间窗口的开始时间,此时窗口向前滑动
} else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {
/**
* 如果原先存在的窗口开始时间小于当前时间戳计算出来的开始时间,则表示 bucket 已被弃用。
* 则需要将开始时间重置到新时间戳对应的开始时间戳
*/
/*
* (old)
* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4
* |_______||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* ... 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 timestamp
* ^
* time=1676
*/
if (updateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
// Successfully get the update lock, now we reset the bucket.
return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);
} finally {
updateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.
Thread.yield();
}
// 这个条件不可能存在
} else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) {
// Should not go through here, as the provided time is already behind.
return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
}
}
}
/**
* 首先用当前时间除以一个时间窗口的时间间隔,得出当前时间是多少个时间窗口的倍数,用 n 表示。
* 然后我们可以看出从一系列时间窗口,从 0 开始,一起向前滚动 n 隔得到当前时间戳代表的时间窗口的位置。
* 现在我们要定位到这个时间窗口的位置是落在 LeapArray 中数组的下标,
* 而一个 LeapArray 中包含 sampleCount 个元素,要得到其下标,则使用 n % sampleCount 即可。
* @param timeMillis
* @return
*/
private int calculateTimeIdx(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) {
// time每增加一个windowLength的长度,timeId就会增加1,时间窗口就会往前滑动一个
long timeId = timeMillis / windowLengthInMs;
// Calculate current index so we can map the timestamp to the leap array.
//上一步的结果可能比窗口个数大或者是窗口倍数,所以要进行求余计算落在了哪个窗口里
return (int)(timeId % array.length());
}1.根据当前时间,算出该时间的timeId,并根据timeId算出当前窗口在采样窗口数组中的索引idx
2.根据当前时间算出当前窗口的应该对应的开始时间time,以毫秒为单位
3.根据索引idx,在采样窗口数组中取得一个时间窗口old
4.循环判断知道获取到一个当前时间窗口
4.1.如果old为空,则创建一个时间窗口,并将它插入到array的第idx个位置,array上面已经分析过了,是一个 AtomicReferenceArray
4.2.如果当前窗口的开始时间time与old的开始时间相等,那么说明old就是当前时间窗口,直接返回old
4.3.如果当前窗口的开始时间time大于old的开始时间,则说明old窗口已经过时了,将old的开始时间更新为最新值:time,下个循环中会在步骤4.2中返回
4.4.如果当前窗口的开始时间time小于old的开始时间,实际上这种情况是不可能存在的,因为time是当前时间,old是过去的一个时间
另外timeId是会随着时间的增长而增加,当前时间每增长一个windowLength的长度,timeId就加1。但是idx不会增长,只会在0和1之间变换,因为array数组的长度是2,只有两个采样时间窗口。至于为什么默认只有两个采样窗口,个人觉得因为sentinel是比较轻量的框架。时间窗口中保存着很多统计数据,如果时间窗口过多的话,一方面会占用过多内存,另一方面时间窗口过多就意味着时间窗口的长度会变小,如果时间窗口长度变小,就会导致时间窗口过于频繁的滑动。
看图理解
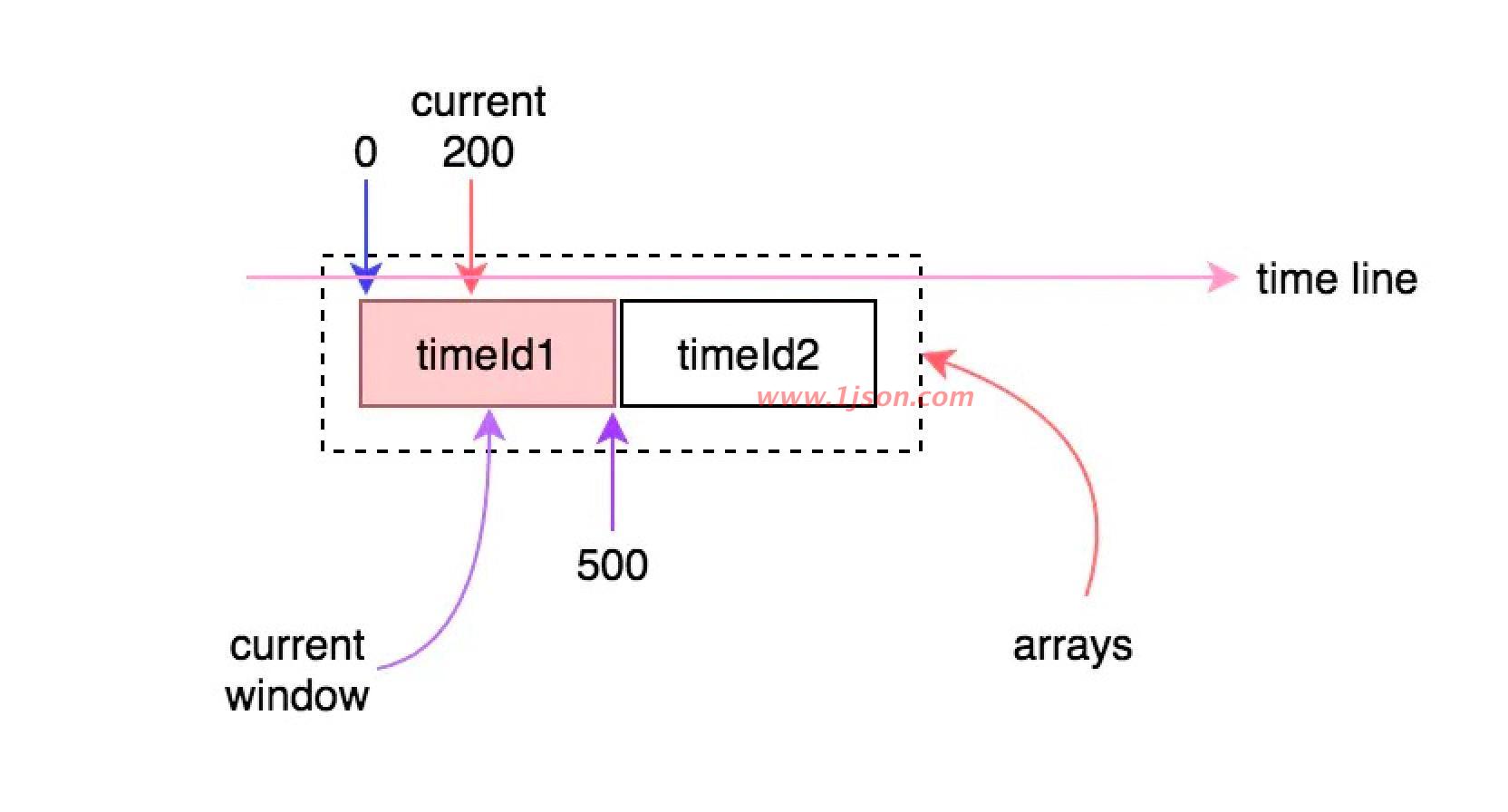
初始的时候arrays数组中只有一个窗口(可能是第一个,也可能是第二个),每个时间窗口的长度是500ms,这就意味着只要当前时间与时间窗口的差值在500ms之内,时间窗口就不会向前滑动。例如,假如当前时间走到300或者500时,当前时间窗口仍然是相同的那个:
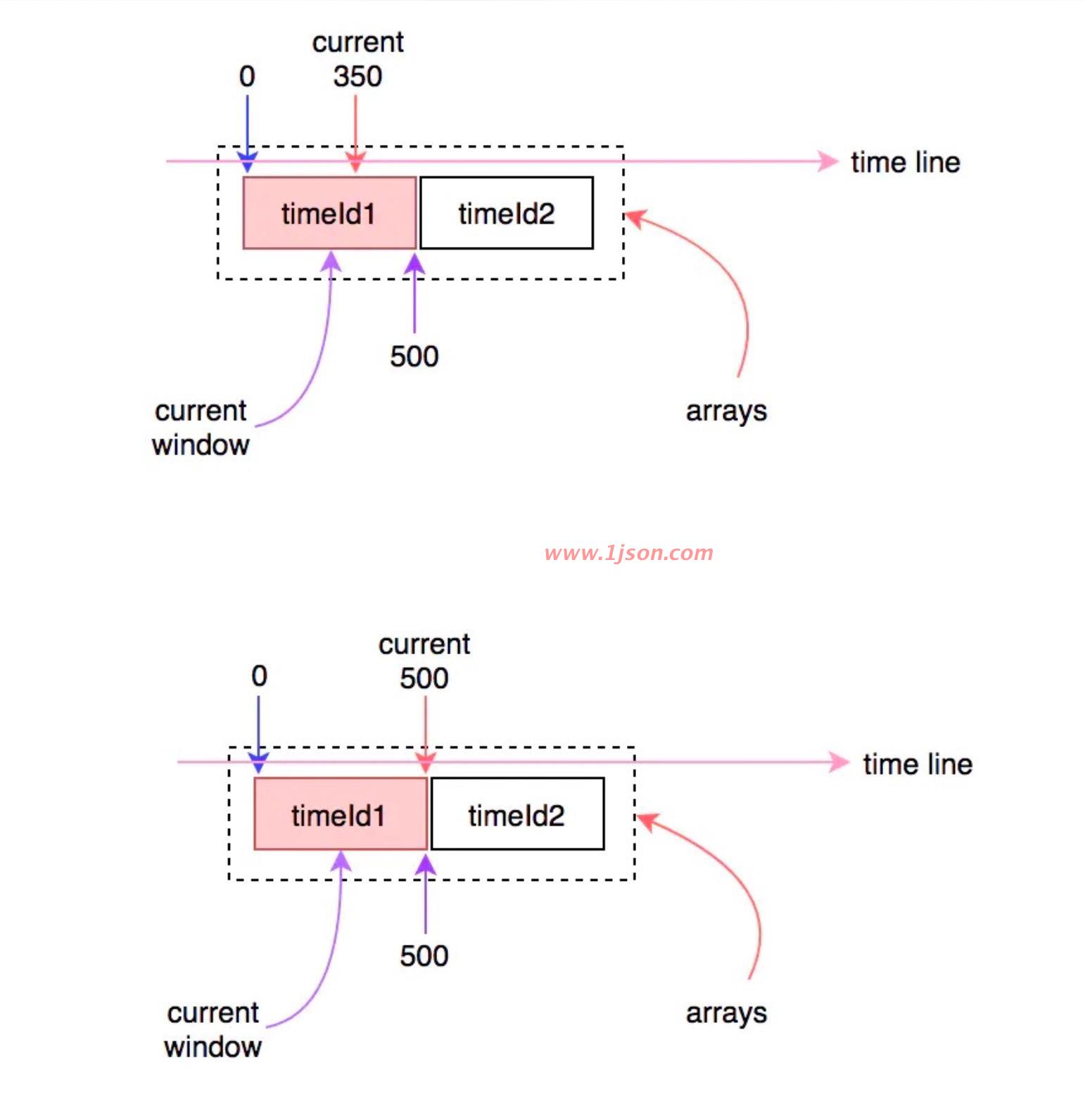
时间继续往前走,当超过500ms时,时间窗口就会向前滑动到下一个,这时就会更新当前窗口的开始时间:
时间继续往前走,只要不超过1000ms,则当前窗口不会发生变化:
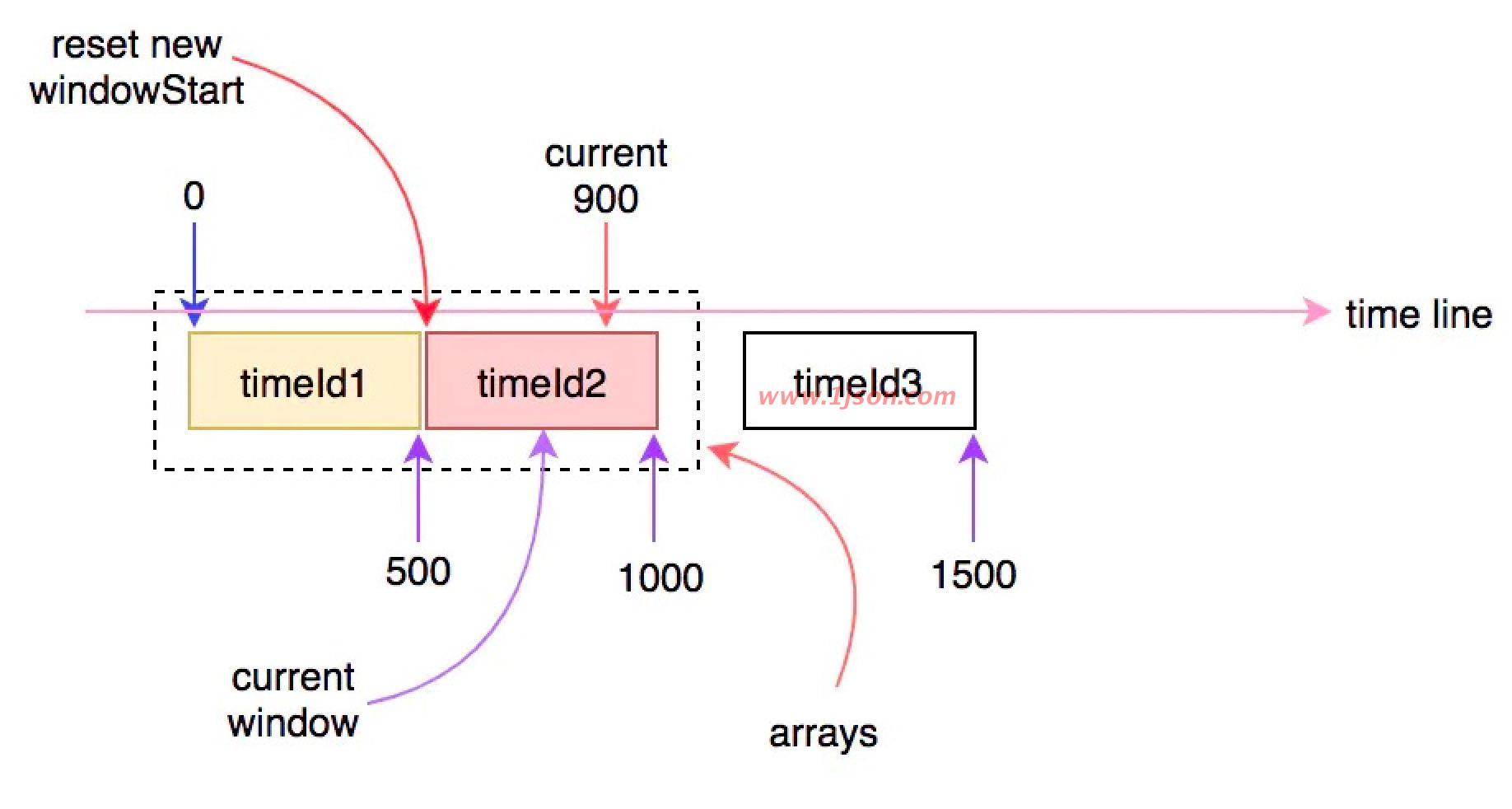
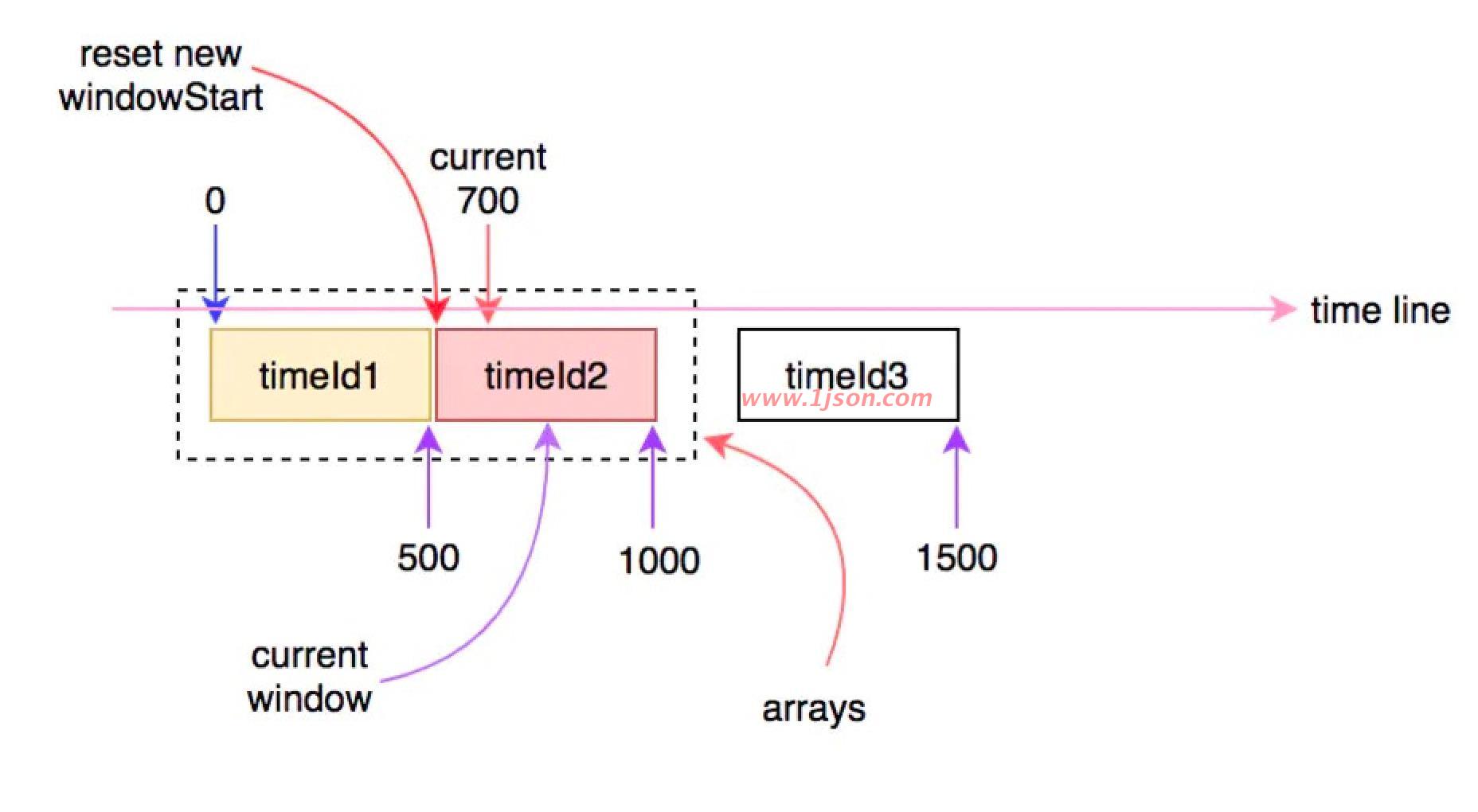
当时间继续往前走,当前时间超过1000ms时,就会再次进入下一个时间窗口,此时arrays数组中的窗口将会有一个失效,会有另一个新的窗口进行替换:
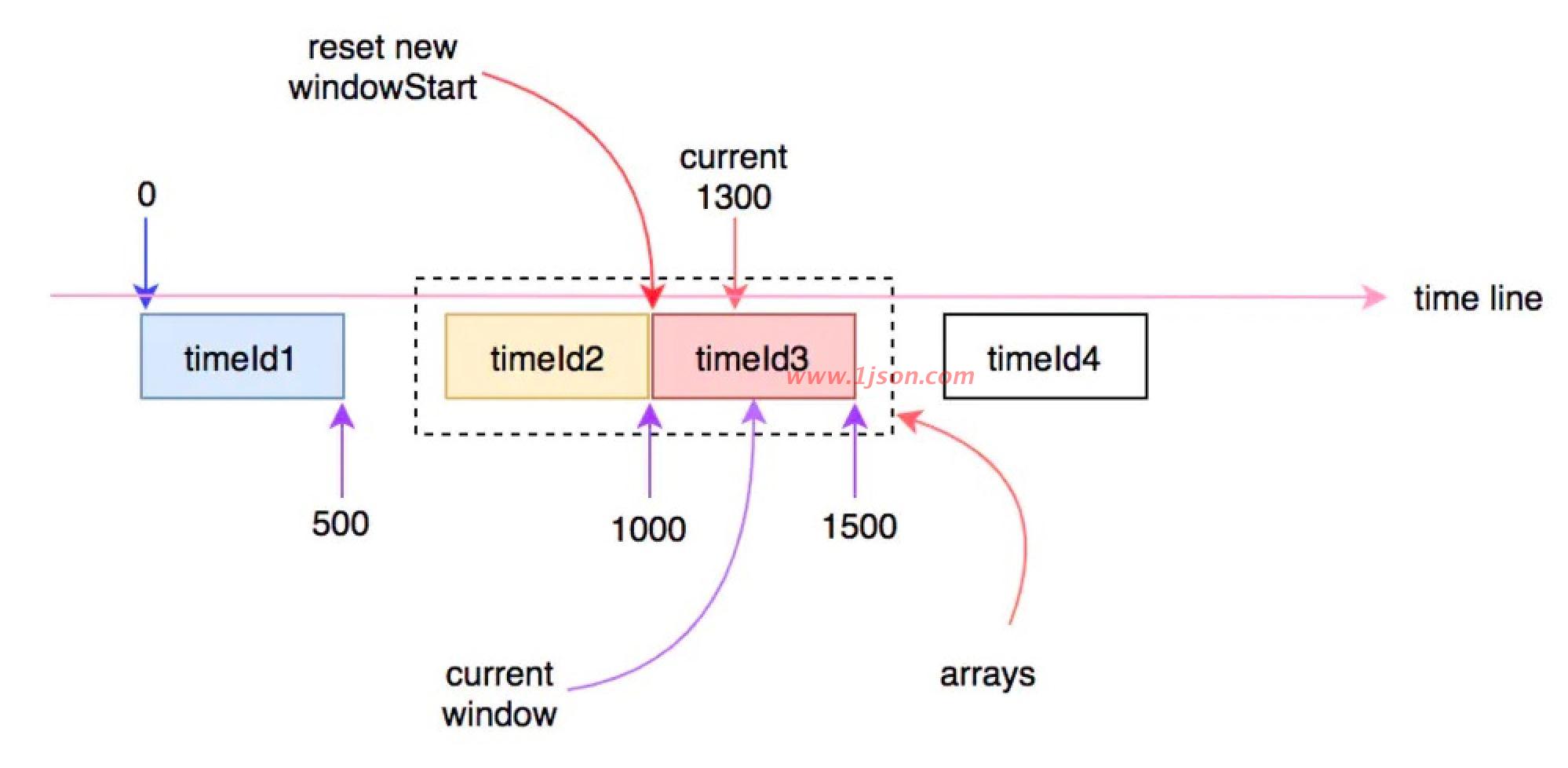
以此类推随着时间的流逝,时间窗口也在发生变化,在当前时间点中进入的请求,会被统计到当前时间对应的时间窗口中。计算qps时,会用当前采样的时间窗口中对应的指标统计值除以时间间隔,就是具体的qps。